About Me

Crystal Ipong
Materials engineering
Crystal Ipong is a senior Materials Engineering Undergraduate Student that is soon to be pursuing a Blended Program for a Polymers and Coatings Masters Degree. She wants to get into industry and potentially become a professor after that. This project was an excellent opportunity to experience developing new educational materials for a class in addition to being exposed to the world of computational modeling and simulation more in depth.
Acknowledgements
I would like to acknowledge the Network for Computational Nanotechnology Undergraduate Research Experience and Undergraduate Computational Education Experience group, Professor Mohsen Kivy, Dr. Tanya Faltens, and the Science Communication Workshop. Their assistance and guidance to this project was invaluable.
“Kinetics of Materials & Process Design” Course Maintains Inclusivity by Virtualizing Learn-by-Doing Lab Component
1. Introduction
Motivation
Learn-by-Doing is a vital part of the Cal Poly curriculum because it prepares students to be ready for their future careers . Working in a computational simulation and modeling technique component into the “Kinetics of Materials Process and Design” course is dual purposed:
- Maintaining inclusivity of the educational opportunity to learn hands-on even in an entirely virtual environment.
- Introducing Materials Engineering students to the field of computational modeling and simulation techniques during their educational careers
Background
- Content: “Kinetics of Material and Process Design” course
- End Users: Junior Level Materials Engineering Undergraduate Students and anyone who wants to familiarize themselves with Kinetics concepts and the tools used.
- How: Hands-on lab component switches from primarily traditional experimentation to the modeling and simulation portion of scientific understanding.
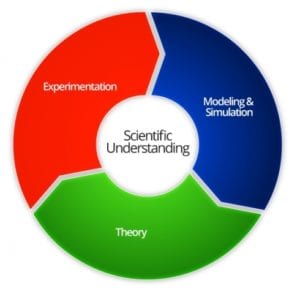
2. Strategy
Tool Discovery and Rating
1. Tool Discovery
Find list of tools with goal of 2 tools per main concept of the kinetics course
2. Ranking Tools
Applying a 1-5 score on key characteristics (i.e. informative, ease of use)
3. Saaty’s Pair Wise Comparison’s
Applying a weighting factor to account for the varying importance between key characteristics (i.e. informative, ease of use)
4. Professor Approval
Kinetics Professor, Dr. Mohsen Kivy, reviewed top-rated tools to determine potential as lab assignment material.
Lab Instruction Development
The lab assignments were designed with following components to promote active learning and “hands on” experience:
- Motivation
- Direct Concept Connection
- Laboratory Instructions
- Deliverables
Lab Instruction Published on nanoHUB
Link: https://nanohub.org/resources/34118/

This project is sponsored by...
3. Example: Phase Transformation Lab
Concept: Phase Transformations
Phase Transformation is one of the main subjects of Kinetics course that describes the transition between different physical states a material may undergo.
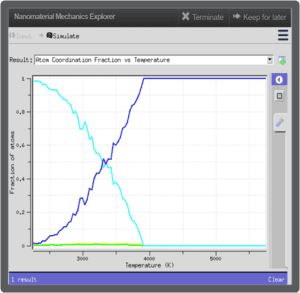
Tool: Nanomaterial Mechanics Explorer
The Nanomaterial Mechanics tool was developed to explore a few topics: tensile tests of nanowires, melting, martensitic phase transformation, crack propagation, and dislocations.
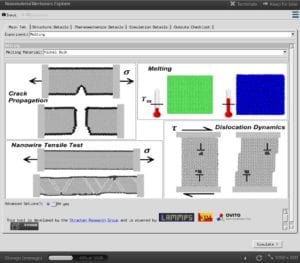
Engineering Concepts Becoming "Hands On"
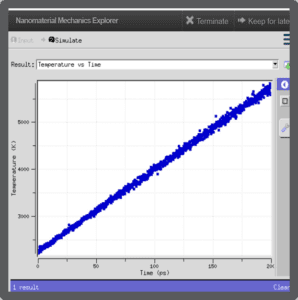
- “Hands on” control of simulation variables: temperature, time, element identity, etc.
- Simulation: provides a visual for students for changing crystal structure of metal polycrystalline structure.
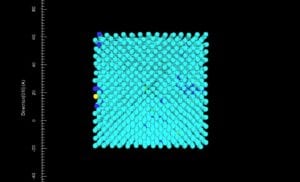
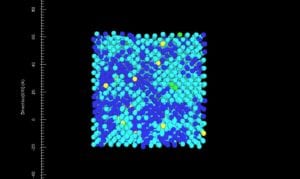

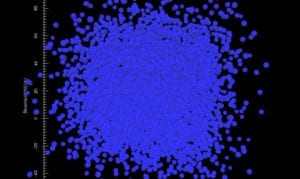
- Class Connection: Students used the Avrami Equation to solve questions.
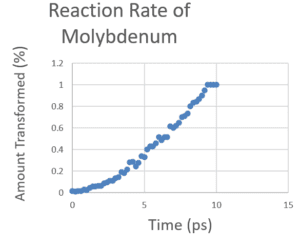
- Deliverables: Questions and tasks were given throughout lab instructions to promote active learning. An example is creating a sigmoidal curve to represent the reaction rate of the melting metal from the simulation data.
4. Tool Summary
Kinetics of Materials and Process Design Course
- Reaction Rates
- Potential Jupyter Notebook
- Solid State Diffusion
- Process Lab: Concentration- Dependent Diffusion
- Process Lab: Defect-couple Diffusion
- Nucleation, Crystallization, and Growth
- Virtual Kinetics of Materials Laboratory: Polycrystalline Growth and Coarsening
- Virtual Kinetics of Materials Laboratory: Dendritic Growth
- Virtual Kinetics of Materials Laboratory: Spinodal Decomposition
- Phase Transformation
- Nanomaterial Mechanics Explorer
5. What is Next for This Project
First Step of an Ongoing Scholarship of Teaching and Learning
- Get feedback after lab assignments implementation to determine effectiveness.
- Some methods of receiving feedback: survey, class discussion
- Use feedback to adjust virtual lab component accordingly.
Future Tool Development
- No tool found that well suited Reaction Rates concept
- Develop Jupyter notebook for Reaction Rates

6. References
The QR code will lead to a document with the nanoHUB tools utilized in this project and sources of images used in poster design.


